Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Introduction of linked list
When we save data in array like data structure then the first element is positioned at first in that array(index 0) then the second element is positioned at second(index 1), third element is positioned at third(index 2) and all other elements are positioned at sequentially.
Now, in this article we will learn about a new data structure name linked list. In linked list, data are not stored in sequentially but in different memory locations. So we can not get data by using index, like array. In here data are linked through pointers.
In details, a linked list is a data structure that consists of a sequence of nodes where each node stores a reference to an object and a reference to the next node in the sequence. It is commonly used for their efficient insertion and deletion operations.
Types of linked list
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
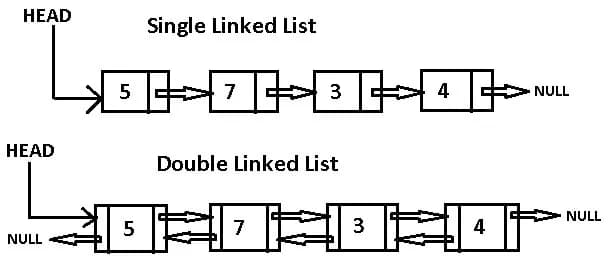
Singly Linked List
A singly linked list is the most basic type of linked list. Each node in the list stores a pointer to the next node in the sequence, except for the last node which stores a null reference.
Implementation
To implement a linked list in javascript we will follow the object-oriented way. So that we need a node class and a linked list class.
Class Node
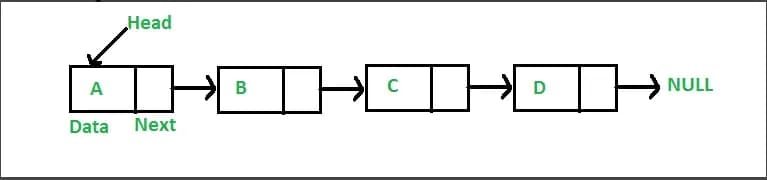
The purpose of the Node class is to represent the individual elements (nodes) that made up the linked list. To represent a node class, we need to have two properties. First is value that will represent the data to be stored and the next the property represents a pointer to the next item in the list.
class Node {
constructor(value, next = null) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}Class LinkedList
The LinkedList class represents a linked list data structure, which is a collection of nodes that are linked together through their next properties. The purpose of the LinkedList class is to provide methods for manipulating the linked list such as adding, updating and deleting nodes. The LinkedList class also has properties such as head, tail and length to keep track of the first and last nodes in the list and the number of nodes in the list respectively.
Initially the first node will become head and tail and also length is set to 1 of the LinkedList class, then in different type of methods we will update these properties periodically.
class LinkedList {
constructor(data) {
let node = new Node(data);
this.head = this.tail = node;
this.length = 1;
}
}Node append method
append(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
this.length++;
} The append method is used for adding a new node at the end of the linked list. In this code snippet:
- The method takes a value parameter which represents the value to be stored in the new node.
- Now we create a new Node object using this value.
- The next property of the current tail node (i.e. the last node in the list) is set to the new node.
- Then the tail property of the LinkedList object is updated to the new node.
- Update the length property by 1.
Node prepend method
prepend(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
this.length++;
}The prepend method is used for adding a new node at the beginning of the linked list. Here are the below steps of how it works:
- This method also takes a value parameter and a new Node object is created with this
valueparameter. - The
nextproperty of the new node is set to the current head node of the linked list. - The
headproperty of the LinkedList object is updated to the new node. - Finally the length property of the object is incremented by 1.
Adding a node at specific position
appendAtPosition(value, n) {
if(n === 1) {
this.prepend(value);
return;
}
if(n > this.length) {
this.append(value);
return;
}
let node = new Node(value);
let prevNode = this.findNode(n-1);
const temp = prevNode.next;
prevNode.next = node;
node.next = temp;
this.length++;
}
findNode(n) {
let data = this.head;
let count = 0;
while(data) {
count++;
if(count === n) {
break;
}
data = data.next;
}
return data;
}In this code snippet:
- The
appendAtPositionmethod takes two arguments: value, which is the value to be added to the list and n, which is the position in the list where the new value should be inserted. - Now, first check if the new node can be added at the beginning of the list (i.e. if
nis 1). If so, it calls theprependmethod to add the new node at the beginning of the list. - Then, check the new node can be added at the end of the list (i.e. if n is greater than the length of the list). In this situation we call the append method.
- If neither of these cases are true, then we create a new
Nodeinstance with the given value. Then call thefindNodemethod to locate the previous node so that the new node can be inserted at the given position. Then assign this node to the variableprevNode. - Now, assign the next node of
prevNodeto a temporary variable temp. Then update the next property ofprevNodeto point to the new node. Finally, update the next property of node to point to the temp variable, which represents the original next node ofprevNode.
Print values of linked list
print() {
let data = this.head;
while(data) {
console.log(data.value);
data = data.next;
}
} In this code snippet: We traverse the list element and printing the value of the property.
Update node at specfic position
update(value, n) {
let node = this.findNode(n);
node.value = value;
}In this code snippet:
First we use the findNode method to locate the node at position n in the linked list. Then simply update the value of node with the new value
Delete node at specfic position
delete(n) {
if (n === 1) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (!this.head) {
this.tail = null;
}
this.length--;
return;
}
let prevNode = this.findNode(n - 1);
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
if (n === this.length) {
this.tail = prevNode;
}
this.length--;
}To properly handle the deletion of a node in the linked list, first we check the node we are deleting is the first node, in that case we update the head property by pointing the next node of head and if there is no second node then we sets the tail property to null. This is necessary because in linked list with only one node, deleting that node should result in an empty linked list where we need to set null in both head and tail.
If the node is not first node then we need to find the previous node and update that next node of previous node.
And finally if n is equal to the length of the linked list then we need to delete the last node as well as need to update the tail.
Reverse a linked list
To reverse a linked list, we will need three pointers: currNode(currentNode), nextNode (null at the start) and previousNode (null at the start).
reverse() {
let currNode = this.head
let nextNode = null
let previousNode = null
while(currNode) {
nextNode = currNode.next
currNode.next = previousNode
previousNode = currNode
currNode = nextNode
}
this.tail = this.head
this.head = previousNode
}