When we solve problems with different type of algorithms, we need to analyze the computational complexity of these solutions. There are two methods for analyzing the complexity of a problem. They are: time complexity and space complexity.
 By Madison Stankevich Dev.to
By Madison Stankevich Dev.to
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Time Complexity
From wikipedia: In computer science, the time complexity is the computational complexity that describes the amount of computer time it takes to run an algorithm. In simple word: time complexity is a measure of how much time an algorithm takes to execute as a function, based on the length of the input. It is usually expressed as a function of the input size, represented by the letter n example: O(n). And we call it order of n or Big (O) of n.
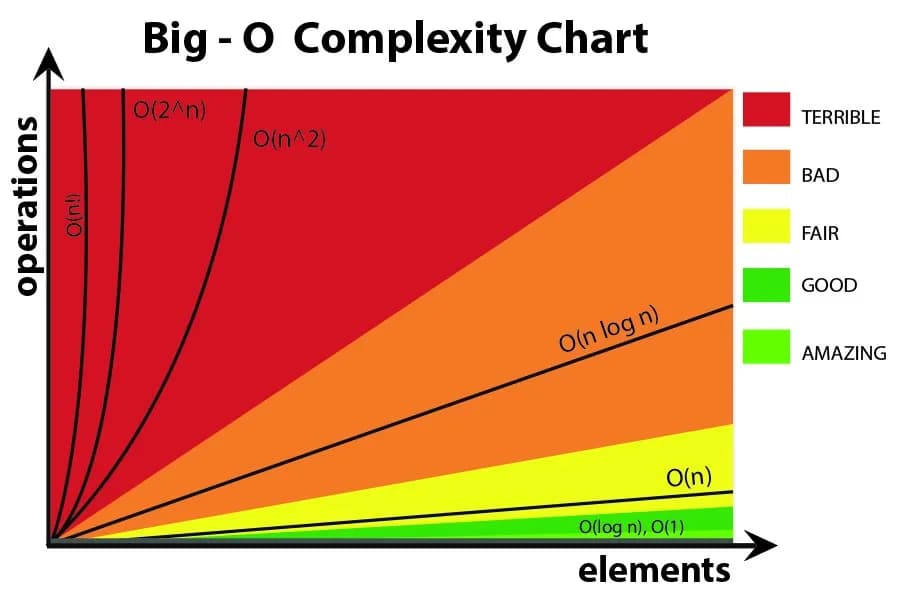
But what is Big(O) and why it is important? In simple terms, if a program can able to handle large amount of input and the amount of time it takes as same as a small amount of input, then we can rate it well according to Big O Notation. Let’s look at the key time and space complexities:
- Constant: O(1)
- Linear time: O(n)
- Logarithmic time: O(n log n)
- Quadratic time: O(n^2)
- Exponential time: 2^(n)
- Factorial time: O(n!)
It’s important to note that time complexity does not measure the actual time an algorithm takes to execute, but rather how the execution time increases with the size of the input. The actual execution time depends on several factors such as the hardware, programming language, and implementation of the algorithm. Enough talking, now let’s take a look at an example below and analysis the time complexity:
let sum = 0
for(let i = N; i > 0; i++)
for(let j = 0; j < i; j++)
sum += 1;Now in the worst case, let’s consider the scenarios:
N*constantoperations will run for input.- The outer loop
iwill run atNtimes. - For each
i, the innerjwill run atNtimes.
So total execution time will beN*N*constant + constant. Now we will ignore the lower order terms as those are relatively insignificant for large inputs, therefore only the highest order term will be taken (without constant) which isN*Nin this case.
Space Complexity
From wikipedia: The space complexity of an algorithm or a computer program is the amount of memory space required to solve an instance of the computational problem as a function of characteristics of the input. In simple word: space complexity is a measure of how much memory an algorithm requires to execute as a function, based on the length of the input. It is also expressed as a function of the input size n. For example, if an algorithm takes O(n) space, it means that the amount of memory it uses grows linearly with the size of the input. For analyzing space complexity of a problem, we need to focus on two parts:
- A fixed part: It is required for storing certain data and variables which are independent of the input size like: simple constants and variables used, instructions(code) etc.
- A variable part: It is required for variables which are dependent on the size of the input like recursion stack, dynamic memory allocation etc. Okay now let’s take a look at an example below and analysis the space complexity:
let sumArray = []
let sum = 0
for(let i = N; i > 0; i++)
for(let j = 0; j < i; j++)
sum += 1;
sumArray.push(sum);The total space required by the code can be calculated as:
Space complexity = size of sumArray + size of sum + size of i + size of j- Since sumArray has a size of
Nand sumiandjare all single integers, the space complexity can be simplified as:Space complexity = N + 3Therefore, the space complexity will beO(N).
Complexity Chart
Data Structure Complexity Chart
| Data Structures | Space Complexity | Average Case Time Complexity | |||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | ||
| Array | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Stack | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Queue | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Singly Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Doubly Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Hash Table | O(n) | N/A | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | O(n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
Search Algorithms
| Search Algorithms | Space Complexity | Time Complexity | ||
| Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | ||
| Linear Search | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Binary Search | O(1) | O(1) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
Sorting Algorithms
| Sorting Algorithms | Space Complexity | Time Complexity | ||
| Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | ||
| Selection Sort | O(1) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Insertion Sort | O(1) | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Bubble Sort | O(1) | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Quick Sort | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Merge Sort | O(n) | O(n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Heap Sort | O(1) | O(1) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
Complexity for Advanced Data Structures
| Data Structures | Space Complexity | Average Case Time Complexity | |||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | ||
| Skip List | O(n log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Cartesian Tree | O(n) | N/A | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| B-Tree | O(n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Red-Black Tree | O(n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Splay Tree | O(n) | N/A | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| AVL Tree | O(n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| KD Tree | O(n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
References
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/time-complexity-and-space-complexity/
- https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/data-structure-tutorial/time-and-space-complexity#GoTop
- https://dev.to/madisonstankevich/big-o-notation-a-brief-overview-for-the-beginner-1o13
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_complexity
- https://flexiple.com/algorithms/big-o-notation-cheat-sheet/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_complexity